CSA Points
What are they, how do you get them, and how to avoid them.
CSA Points
First, some definitions
FMCSA
FMCSA stands for the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration. This is a federal government agency responsible for overseeing motor carriers across the country.
CSA
CSA stands for the Compliance, Safety, Accountability program. This program is is administered by the FMCSA. The CSA program is a way for the FMCSA to track and rank motor carriers to determine if the FMCSA needs to take action against the motor carrier for unsafe driving.
CSA Points
Just like a state MVD may assign points to a driver’s license based on the severity of traffic violations the driver commits, the FMCSA assigns points to violations committed by commercial truck drivers and motor carriers.
Safety Measurement System (SMS).
This is where the FMCSA stores CSA program information.
BASICS
CSA points can be applied in seven different categories, called “Behavior Analysis and Safety Improvement Categories”, or BASICSs. These 7 categories are:
-
- Unsafe driving – includes moving violations like speeding or holding a mobile device whild driving
- Crash indicator – includes crash history
- HOS compliance – HOS violations or logbook violations
- Vehicle maintenance – includes not only vehicle maintenance but improperly secured loads
- Controlled substance/alcohol – DUI or even just possession of alcohol or drugs in a CMV
- Hazardous materials compliance – unsafe handling of hazardous materials
- Driver fitness – includes lack of required CDL
What does the FMCSA do with CSA Points?
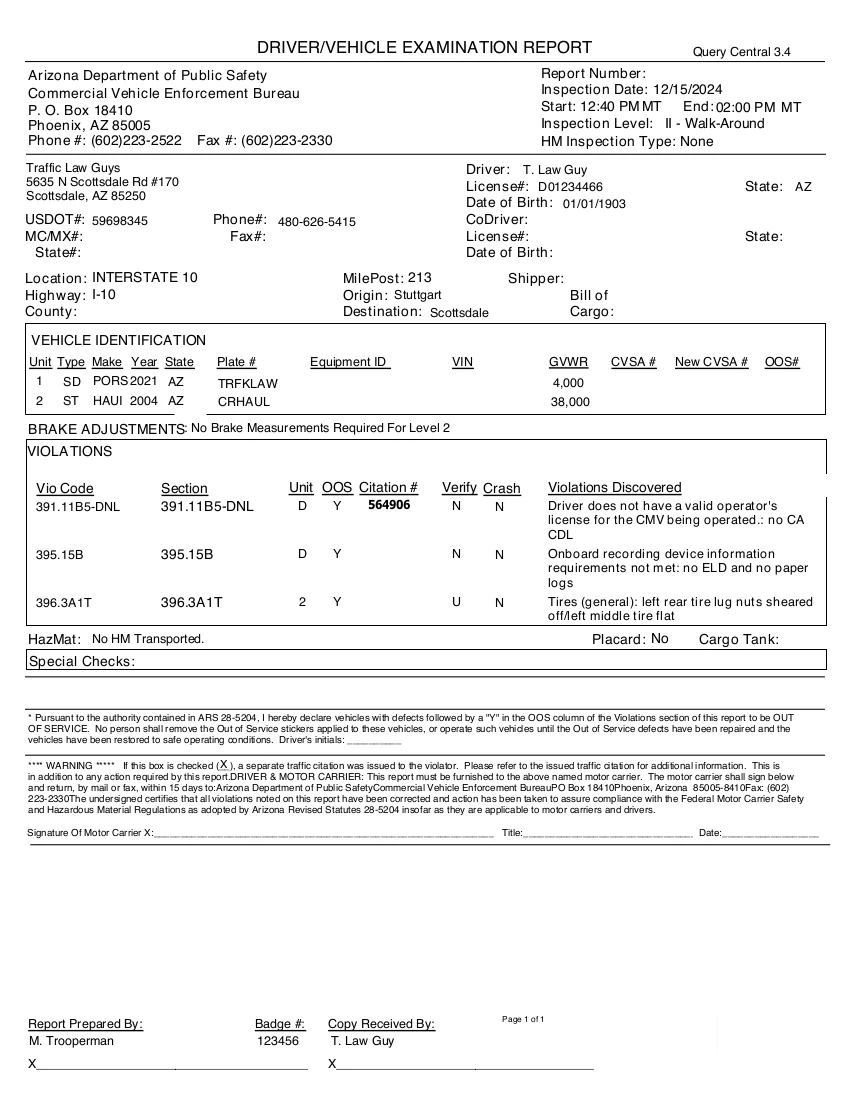
In a nutshell, any violations that are reflected on a Driver Examination Report, or DVER (said dee-ver) result in CSA points. These points apply to the motor carrier though, not the driver. This is why at the bottom of a DVER, there is a statement about the motor carrier needing to sign and return the DVER to the law enforcement agency that conducted the inspection.
The points applied to a motor carrier are used to rank the motor carrier in relation to other motor carriers. This is a percentile rank from 0 to 100%. An excellent rank would be zero, and the worst rank would be 100%. If a carrier has a rank of 100%, that means as far as FMCSA is concerned, that motor carrier is the most unsafe motor carrier on the road.
The ranking is updated monthly.
How do you get rid of CSA points?
Really the only successful way to do this is 1) if there is a ticket issued with the DVER, you can 2) fight the ticket in court, and 3) if you win, 4) correct the DVER through the DataQs system.
Why CSA Points Matter
CSA Points Could Affect Driver Employment
While drivers don’t have a CSA score or rank, only motor carriers do, CSA points can impact empl0yment.
Drivers do have a PSP record – a “Pre-employmeht screening program” record. This record shows the last 5 years of crash history and 3 years of roadside inspection history.
A motor carrier’s CSA rank is made up of the points accumulated by the carrier and its drivers.
So a driver who has a bad CSA points history may run into problems trying to get a job with certain motor carriers.
A Bad CSA Rank Makes Drivers A Target Of Law Enforcement
A CSA percentage rank greater than 65% in the unsafe driving, crash indicator, and HOS categories are subject to FMCSA investigations. Hazardous materials and passenger carriers categories have lower threshholds of 60 and 50% respectively.
The remaining categories have an 80% threshold.
If law enforcement sees a DOT number on a vehicle for a carrier with a bad CSA rank, law enforcement will inspect that vehicle. So drivers who work for carriers with bad CSA ranks are automatically targets for law enforcement action.
A Good CSA Rank Benefits Carriers
For example, carriers with good CSA scores benefit from:
- Lower insurance premiums
- Fewer DOT audits
- Fewer roadside inspections
- Better reputation with current and potential customers
- Attracts better drivers
CSA Points Examples
In addition to points, there is also an Acute and Critical sub-category of violations added to each BASIC category. Any acute/critical violations automatically create flags against a carrier in the Safety Measurement System.
Driving/Moving Violations
10-Point Violations
- Using a hand-held mobile telephone while operating a CMV—393.82(a)(1)
- Texting While Operating a CMV—390.33-XS
- State/Local Laws—Operating a CMVwhile texting—392.2-SLLS2
- Reckless driving—392.2R
- Speeding 15 or more mph—392.2
- Speeding in construction zones—392.2-SLLS4 (State and Local Laws)
8-Point Violations
- Unqualified driver—391.11
7-Point Violations
- Speeding 11 to 14 mph—392.2-SLLS3
- Fail to use seat belt while driving a CMV—392.16
5-Point Violations
- Failure to obey a traffic control device—392.2
- Following too close—392.2
- Improper lane change—392.2
- Improper passing—392.2
- Using or equipping a CMV with radardetector—392.71(a)
4-Point Violations
- Speeding between 6 and 10 mph—392.2
2-Point Violations
- Lacking physical qualifications—391.11
Critical Violation
- Operating a commercial motor vehicle not in accordance with the laws, ordinances, and regulations of the jurisdiction in which it is being operated—392.2
Hours of Service Violations
10-Point Violations
- Operating a CMV while ill or fatigued—392.3
7-Point Violations
- Violating state and/or local hours of service (HOS) laws—392.2
- 15, 20, 70/80 HOS violations (Alaska-Property)—395.1
- 16-hour rule violation—395.1
- Requiring or permitting a driver to drive over 11 hours—395.3
- 11-hour rule violation—395.3
- Requiring or permitting a driver to drive past 14 hours on-duty—395.3
- 14-hour rule violation—395.3
- 60/70 hour rule violation—395.3
- 34-hour restart violation—395.3
- Violating HOS (transportation of migrant workers)—398.6
Critical
- Requiring or permitting a driver to drive more than 10 hours—395.3(a)(1)
Driver Fitness
10-Point Violations
- Operating a CMV while possessing a fraudulent medical certificate—390.35B-MED
8-Point Violations
- Driver operating a CMV without proper endorsements or in violation of restrictions—391.11B5-DEN
4-Point Violations
- Driver cannot read or speak the English language sufficiently to respond to official inquiries—391.11(b)(2)
- Driving a CMV in Interstate Commerce and driver is less than 21 years of age—391.11(b)(1)
1-Point Violations
- No medical certificate in driver’s possession—391.41(a)
Vehicle Maintenance
8-Point Violations
- Flat tire or fabric exposed—393.75(a)
6-Point Violations
- Inoperative turn signal—393.9TS
- Inoperable tail lamp—393.9T
- Operating CMV with lamps/reflectors obscured—392.33
3-Point Violations
- No or defective lighting devices orreflective material as required—393.11
1-Point Violations
- Passengers not protected from fallingbaggage (bus)—392.62(c)(3)
Critical
- Failing to keep minimum records of inspection and vehicle maintenance—396.9(c)(2)
Controlled Substances and Alcohol
10-Point Violations
- Driver uses or is in possession of drugs—392.4(a)
5-Point Violations
- Driver consuming an intoxicating beverage within 4 hours before operating a motor vehicle—392.5(a)
3-Point Violations
- Driver having possession of alcohol while on duty, or operating, or in physical control of a CMV—392.5A2-POS
Critical
- Using a driver before the motor carrier has received a negative pre-employment controlled substance
test result—382.301(a)
Hazardous Materials (HM) Compliance
10-Point Violations
- Packaging not authorized by the Hazardous Materials Regulations—173.24(c)
- Package not secure in-vehicle—177.834(a)
8-Point Violations
- Tank outlets not marked—178.245-6(b)
7-Point Violations
- Damaged liquid discharge hose—180.416(g)
4-Point Violations
- Fail to possess remote shutoff when unloading—177.840(s)
Critical
- Failing to provide security awareness training—172.704(a)(4)
CSA Points Multiplier
Violations for drivers are multiplied based on how recently it occurred.
- Violations within 12-24 months are counted once.
- Violations within 6-12 months are multiplied by 2
- Violations within 0-6 months are multiplied by 3
FAQs
Do Driver's Have A CSA Score Or Rank?
No, only motor carriers have a CSA ranking. However, drivers still need to worry about CSA points, because a motor carrier’s rank depends on the CSA points assigned to the violations a driver has accumulated.
How Often Are CSA Rankings Updated?
CSA percentage rankings are updated monthly.
How Can You Look Up A Motor Carrier's CSA Ranking?
You can look up a motor carrier’s CSA ranking at https://csa.fmcsa.dot.gov/
How do you get CSA points?
CSA points are associated with violations noted on a driver vehicle examination report, or DVER. Violations that are listed on a traffic ticket and complaint do not have CSA points. Violations on a DVER do not have points in the traditional sense that impact a driver’s state-issued license.
Violations on a traffic ticket are not reportable to the CSA SMS system, and violations on a DVER are not reportable to a state MVD.
Have a Question?
Send us an email below.
Latest Blog Posts
How Not To Get Pulled Over By The Cops
When you're out driving around, the last thing you want to deal with is an encounter with the police. For most of us, a police encounter begins with a traffic stop. Not only do you not want to deal with the delay of a traffic stop or the fines and points from a...
Change of Plea Hearing
Misdemeanor Change Of Plea Hearing In Arizona What to expect at a change of plea hearing. What is a change of plea hearing? A change of plea hearing is a hearing held by the court wherein the defendant changes his or her plea. Typically, a defendant will plead "not...
Chris Rike is a founding partner of Traffic Law Guys, an Arizona law firm committed to protecting the rights of drivers facing criminal traffic charges.


